LEARN DETAILS
LEARN DETAILSEasy Solar Kit
Monitoring & Accessory
- Monitoring & Accessory
- Smart Meter
MH2000/MH1000
- Power meter
MH2000/MH1000
- DTU
MH2000/MH1000
- Hang on Balcony (DIY)
-
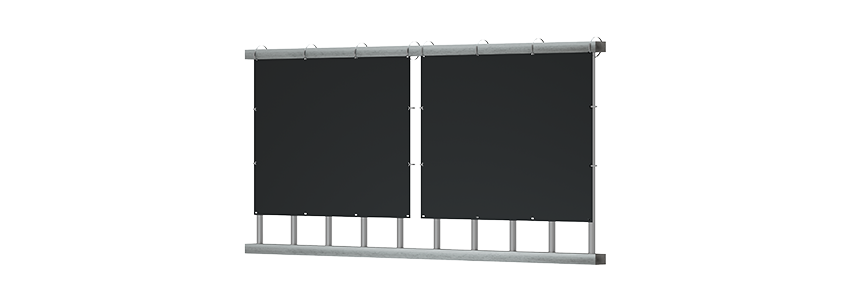
ESK Balcony Air Vertical
ESK400/800-Air(V)
-
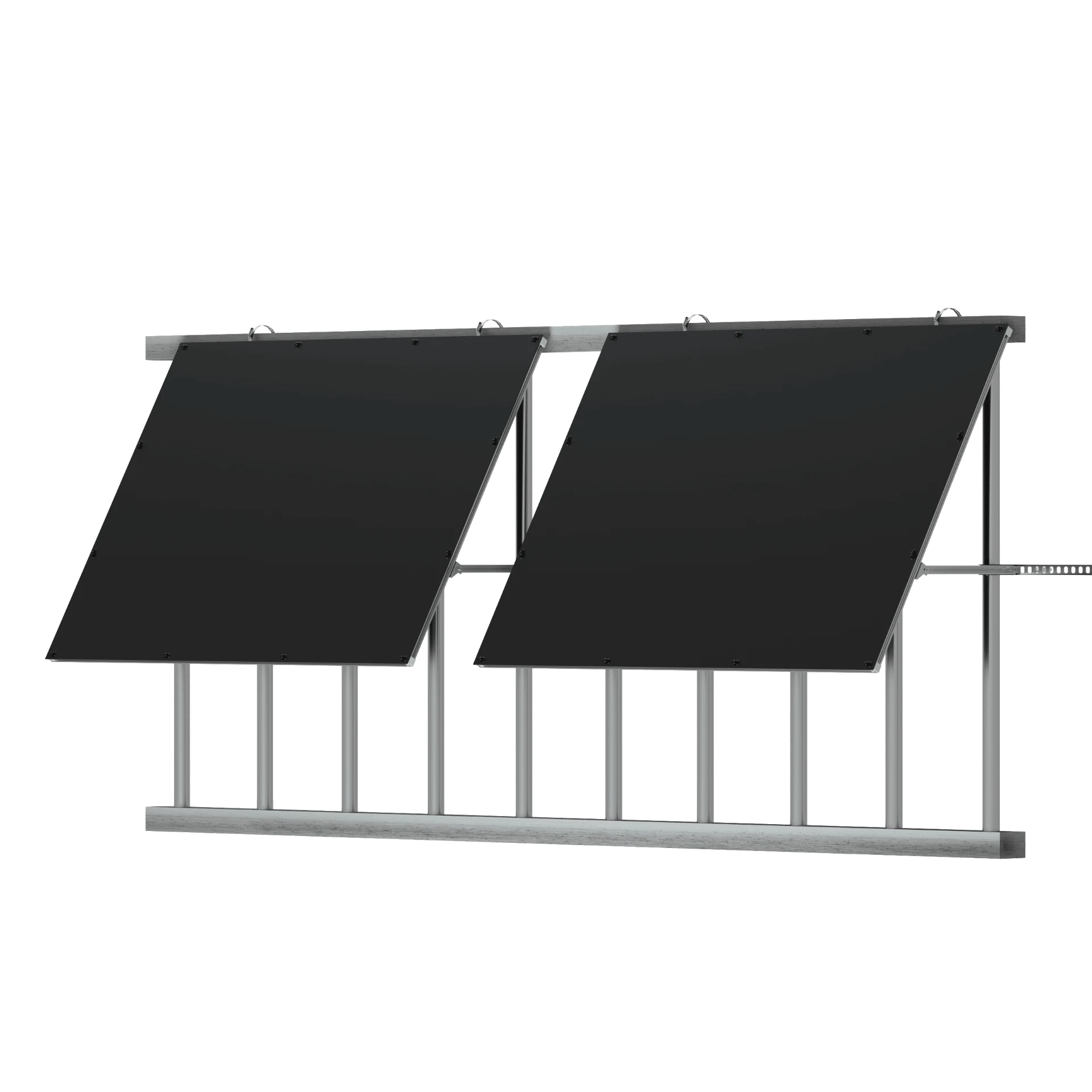
ESK Balcony Air Angled
ESK400/800-Air(A)
-

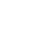
ESK Balcony Vertical
ESK400/800-BV
-

ESK Balcony Angled
ESK400/800-BA
- On the Ground (Ready to Use)
-

ESK Pop-Up
ESK400/800-P
- All Scenarios (DIY)
-
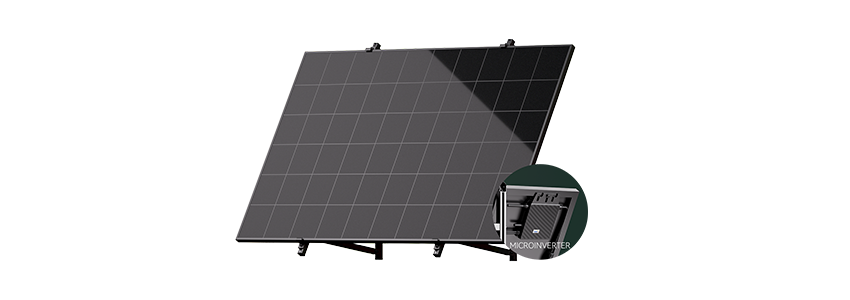
ESK Universal
ESK400/800-U
-
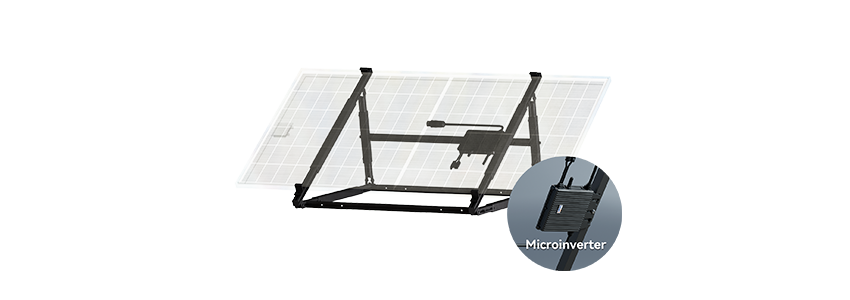
ESK Transformer
ESK400/800-T
- Micro Storage System
-

SolarTrunk (Micro Hybrid Storage Unit)
MSU2000/2000DE | 2 kWh - 10 kWh
-

PowerTrunk (Micro AC Coupled Unit)
MAU2000/2000DE | 2 kWh - 10 kWh
-

SolarCan (DC Coupled Unit)
DCU2000Lite | 2 kWh - 10 kWh
-

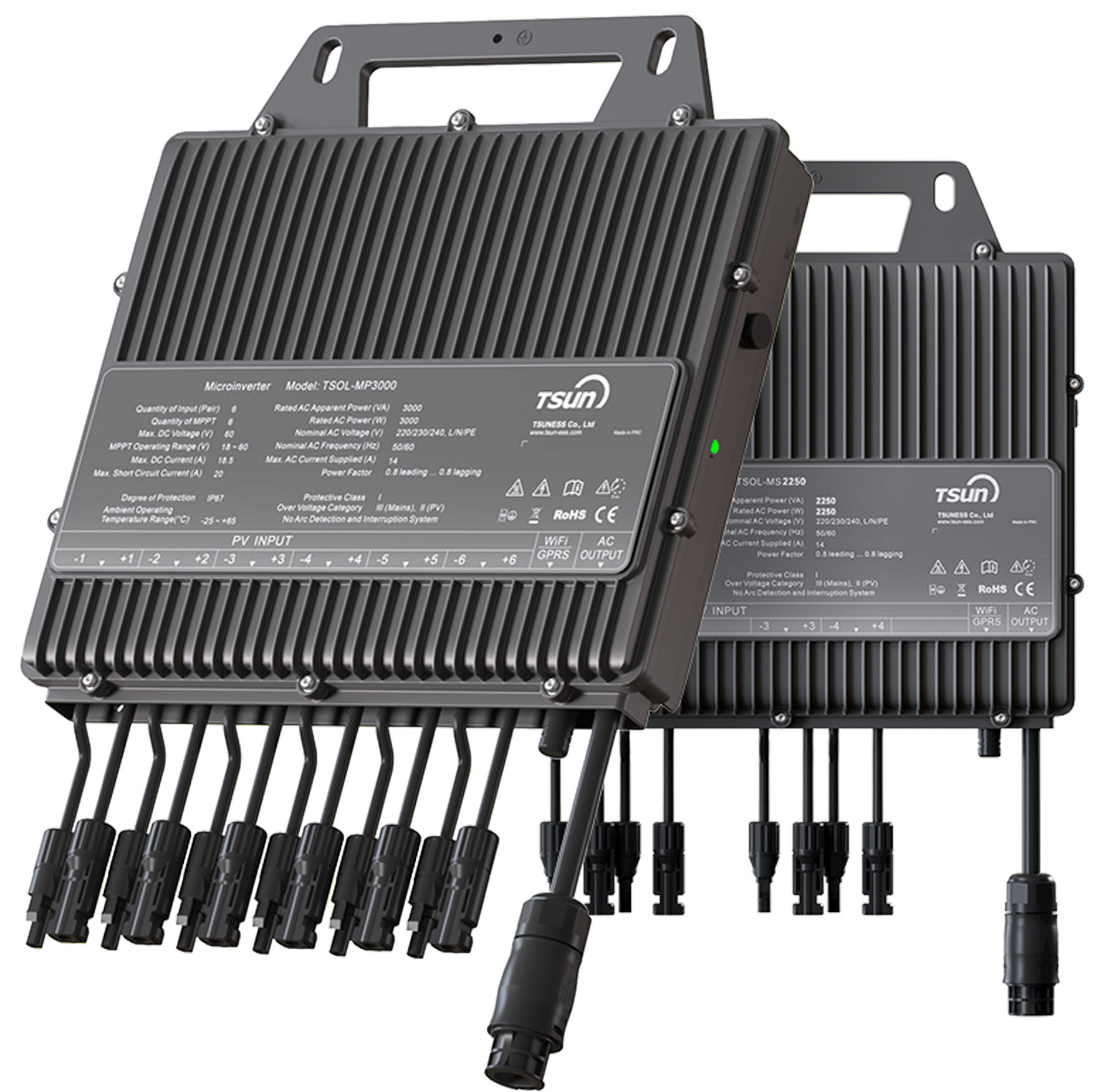
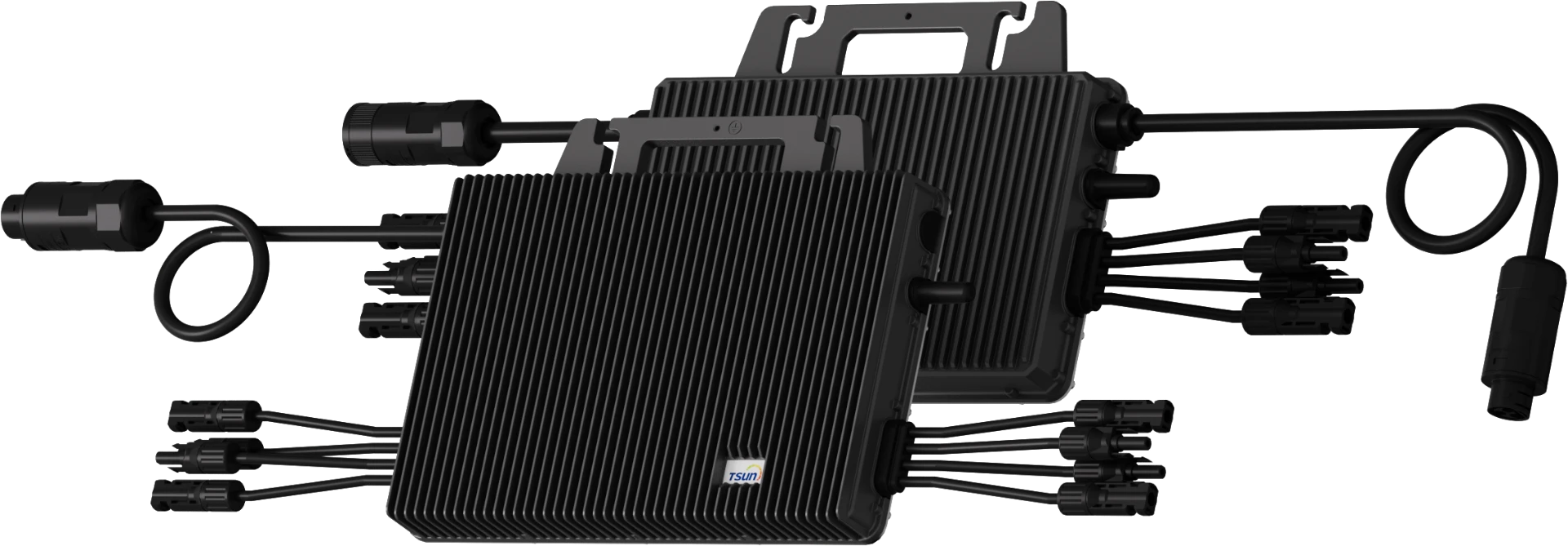
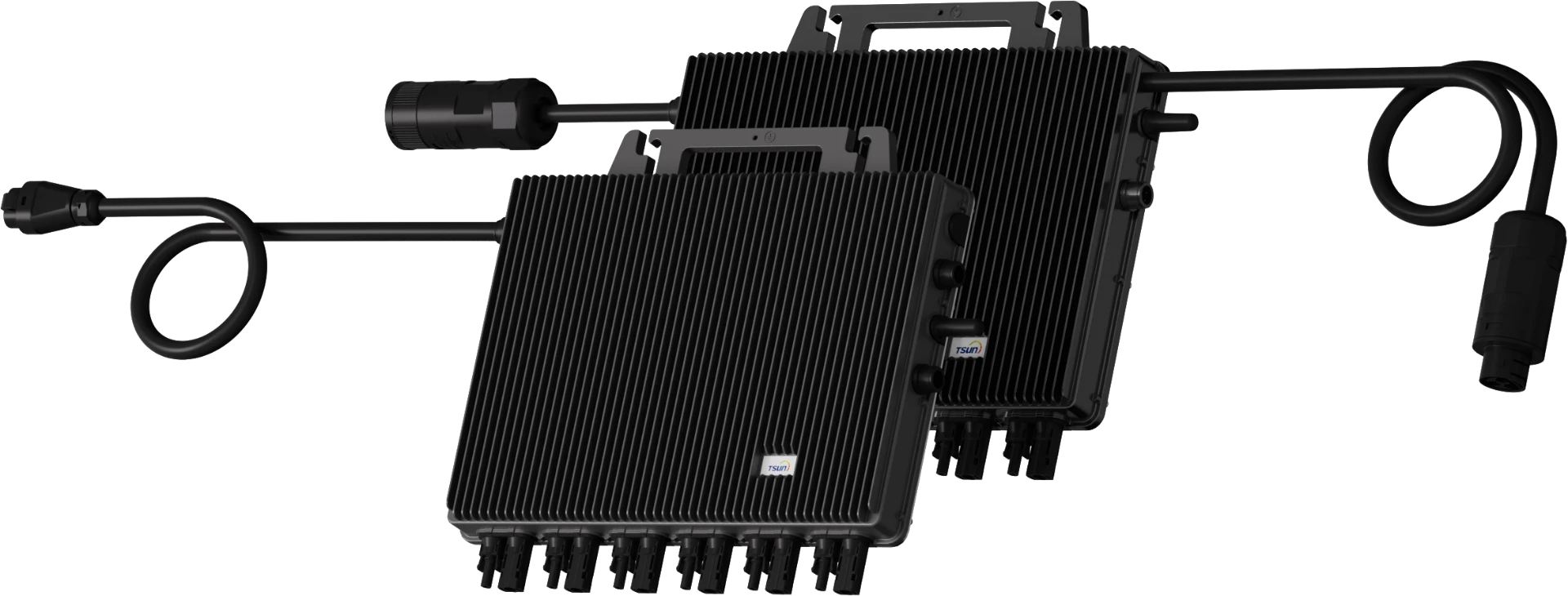
Hybrid Microinverter
MH2000/MH1000
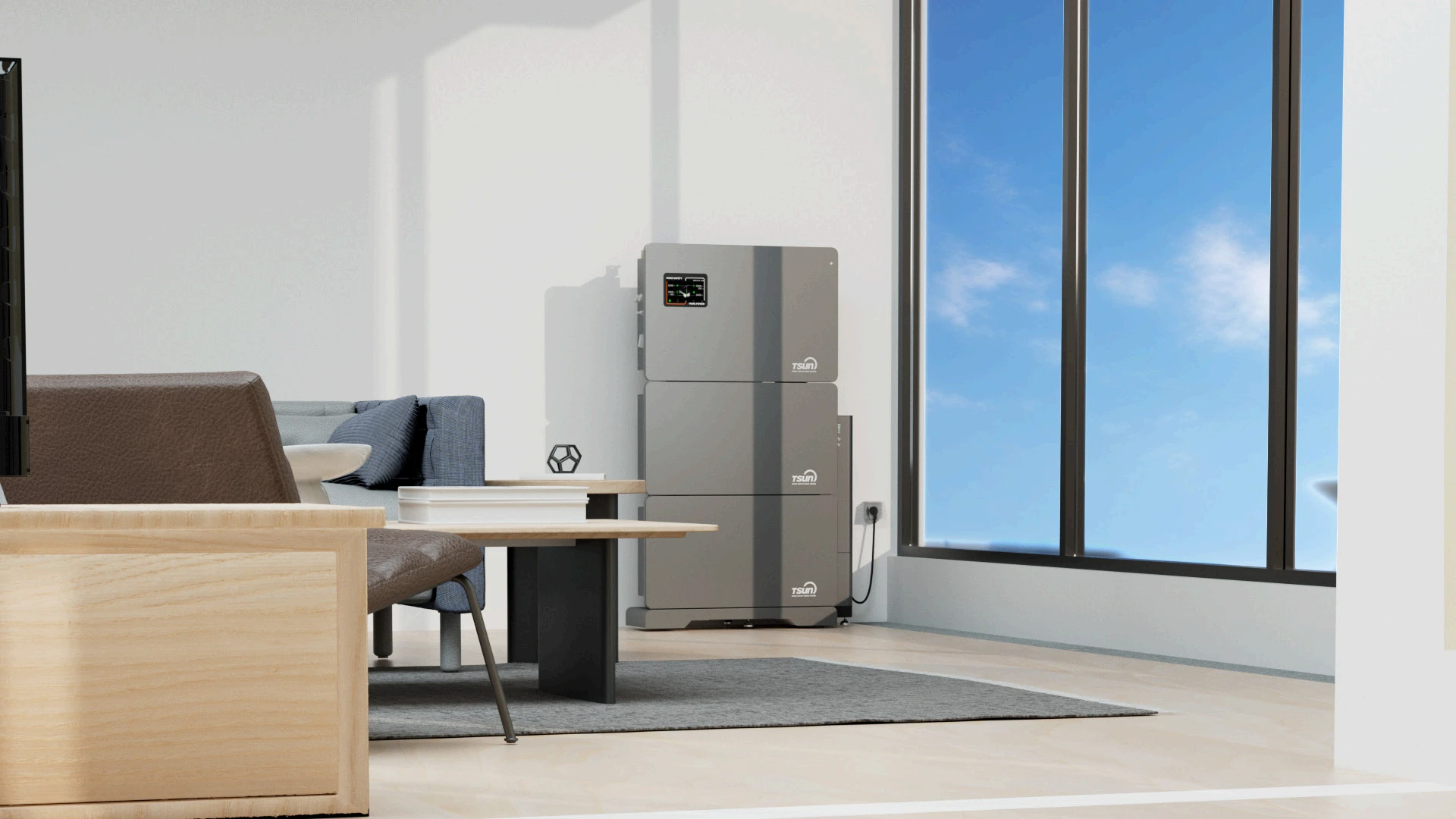
- Residential Storage System
-
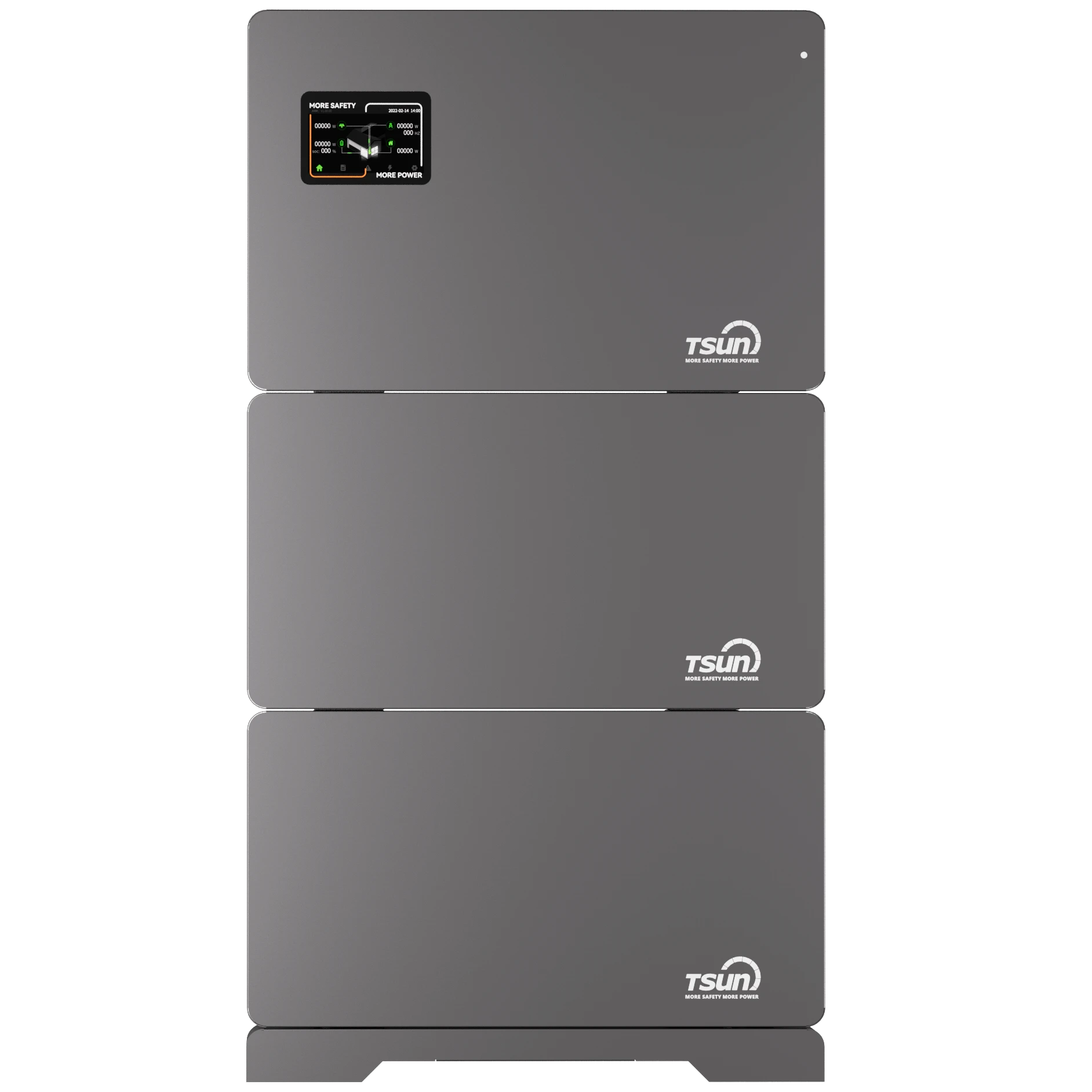

AC Coupled Storage Unit
ACU3.0/3.6/4.0/4.6/5.0/6.0K | 5 kWh-20 kWh
- Monitoring & Accessory
-
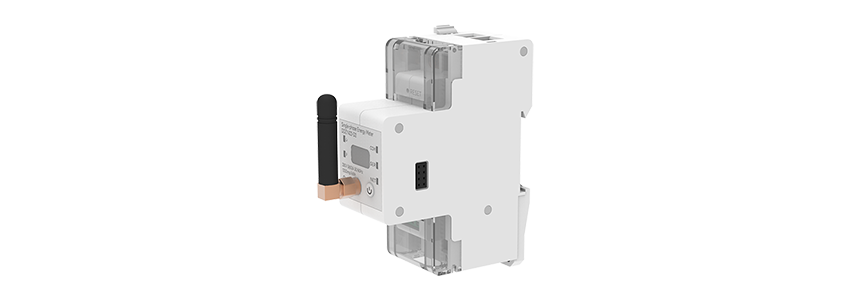
Smart Meter
Built-in Wi-Fi
-

Power meter
Built-in RS485/CT
-

DTU
Built-in Wi-Fi & RS485 & RJ45
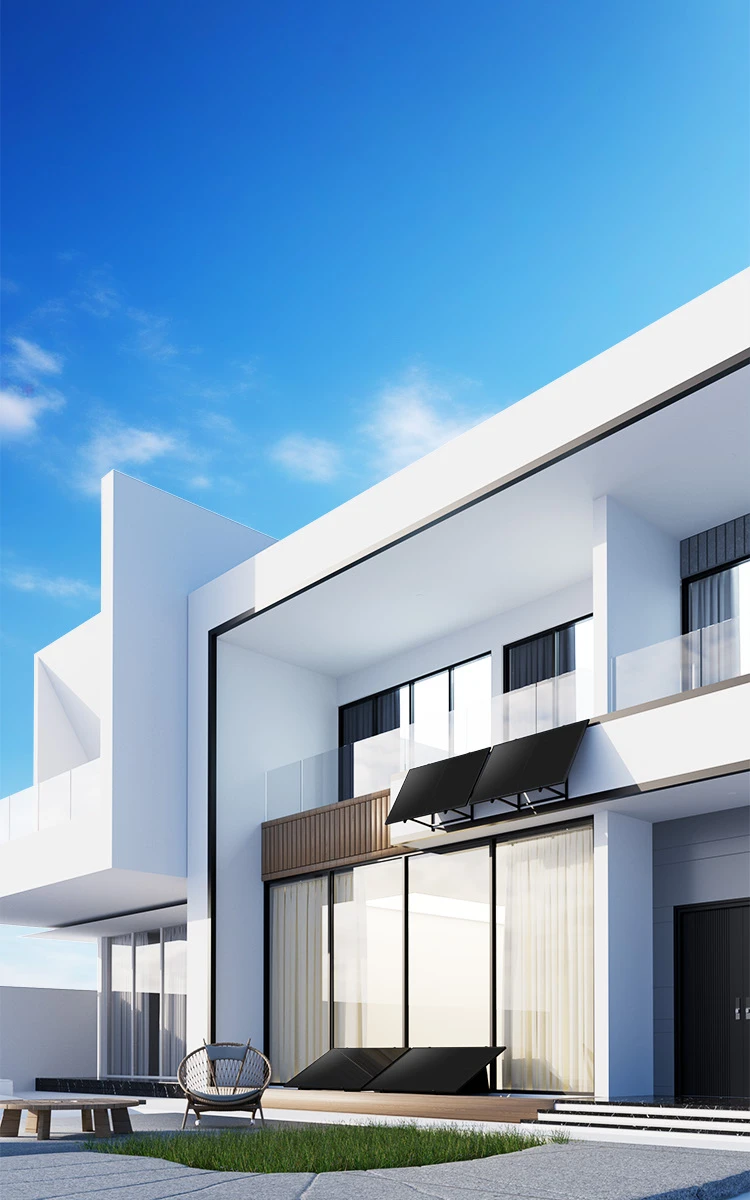

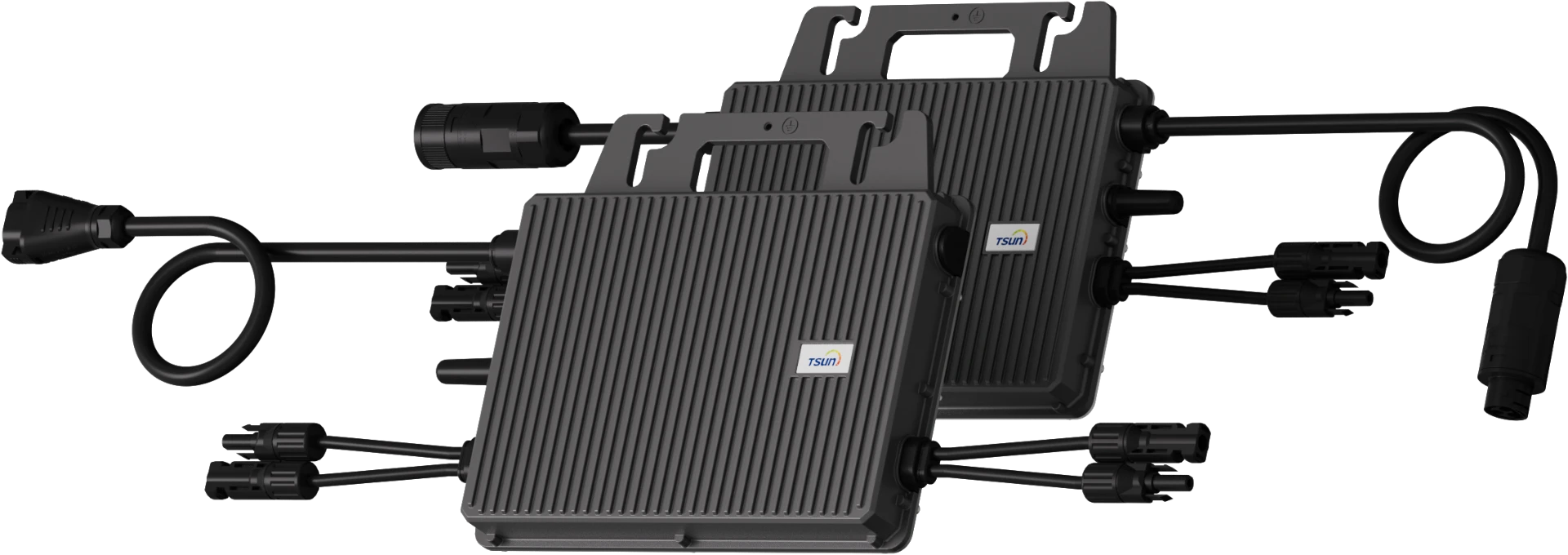
On Grid System — Easy Solar Kit
Easy Solar Kit, which integrates PV module, microinverter, DIY bracket and cables, is designed for a variety of applications, can be installed on balcony, garden, flat roof and even wall.
 LEARN DETAILS
LEARN DETAILS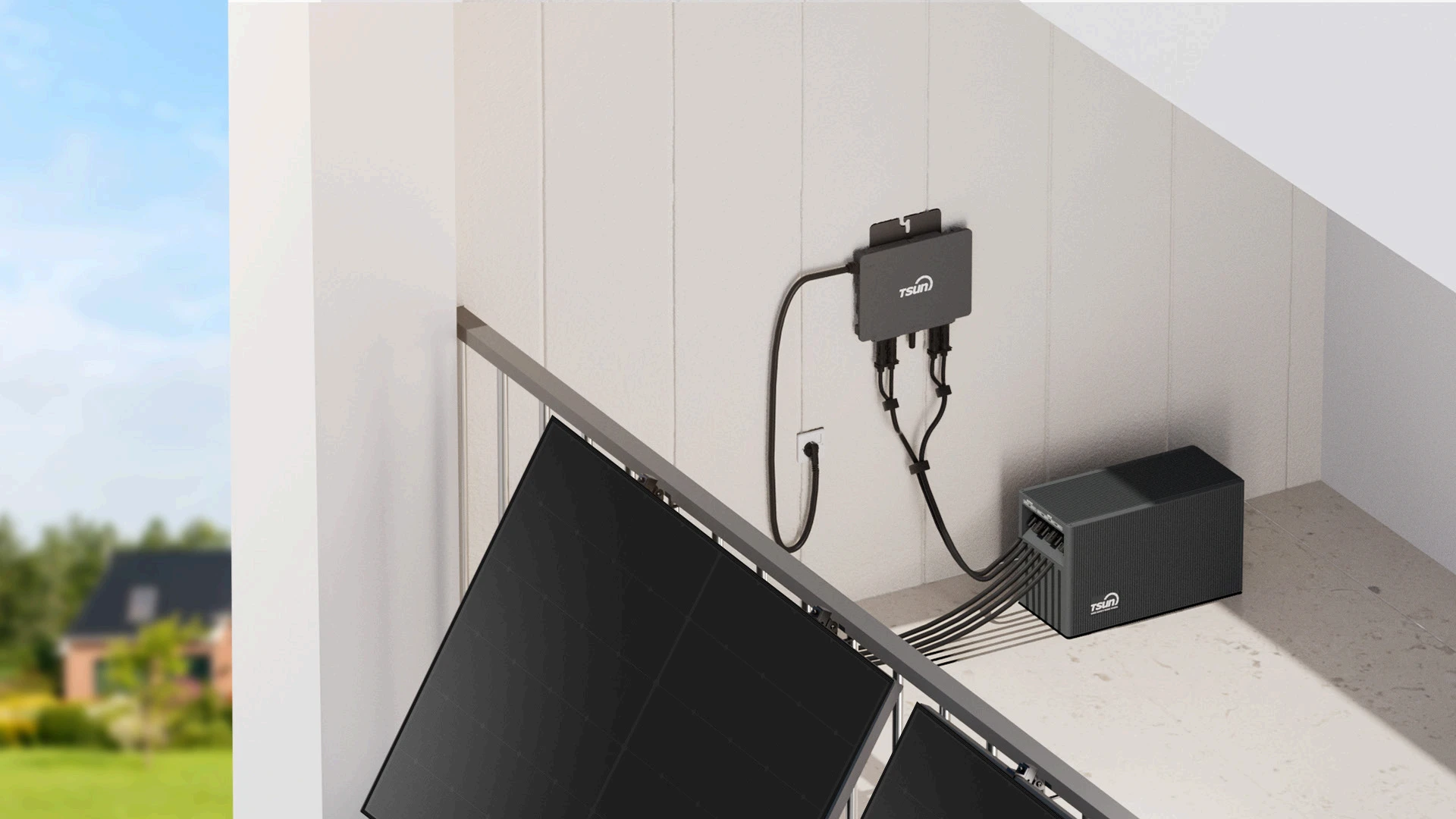
Storage System — SolarCan(DC Coupled Unit) & Easy Solar Kit
This solution, Solar Module + SolarCan + Balcony Microinverter, is typically used as a micro energy storage solution for small household, conventional balconies, courtyards, family carports, and other plug & play scenarios.
 LEARN DETAILS
LEARN DETAILS
Storage System — Hybrid Microinverter & Stackable Battery Pack & Easy Solar Kit
The integrated configuration of solar modules, hybrid microinverters, and batteries serves as a versatile hybrid energy storage solution, predominantly deployed in diverse residential settings, including balconies, courtyards, and house carports.for small household, conventional balconies, courtyards, family carports, and other micro systems.
 LEARN DETAILS
LEARN DETAILS
SolarTrunk(Micro Hybrid Storage Unit) & Easy Solar Kit
The SolarTrunk is designed to store surplus electrical energy within the battery and discharge it as required. This integrated configuration of solar modules and the SolarTrunk functions as a versatile hybrid energy storage solution, predominantly deployed in diverse residential settings, including balconies, courtyards, and house carports
 LEARN DETAILS
LEARN DETAILS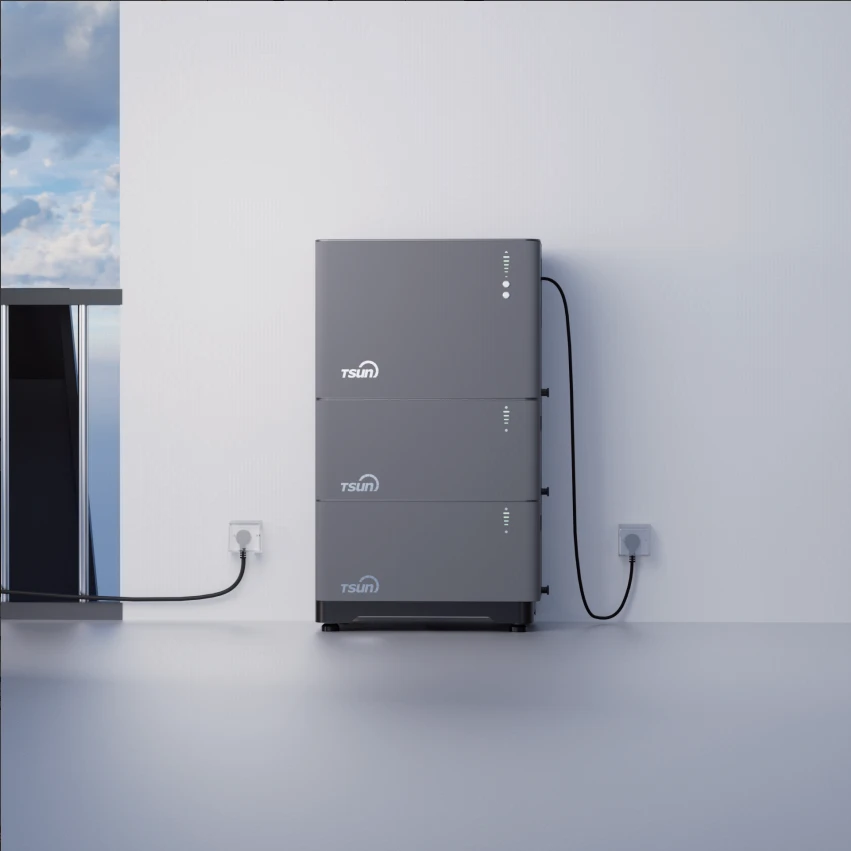
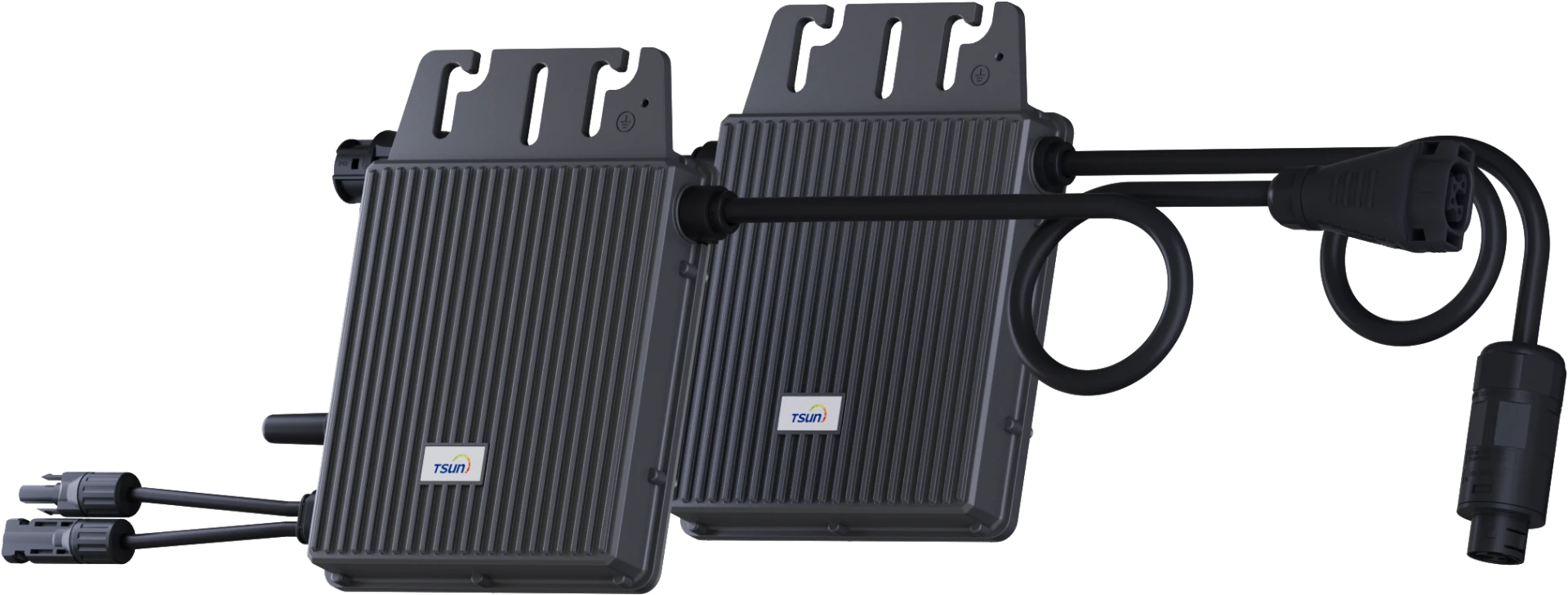
PowerTrunk(Micro AC Coupled Unit) & Easy Solar Kit
The PowerTrunk is a key component of the micro hybrid storage system, which integrates both the energy storage inverter and the battery pack.
 LEARN DETAILS
LEARN DETAILS








 Downloads
Downloads Video Center
Video Center Report Fault for Repair
Report Fault for Repair FAQS
FAQS Service Network
Service Network Privacy Policy
Privacy Policy Contact Us
Contact Us Monitoring
Monitoring

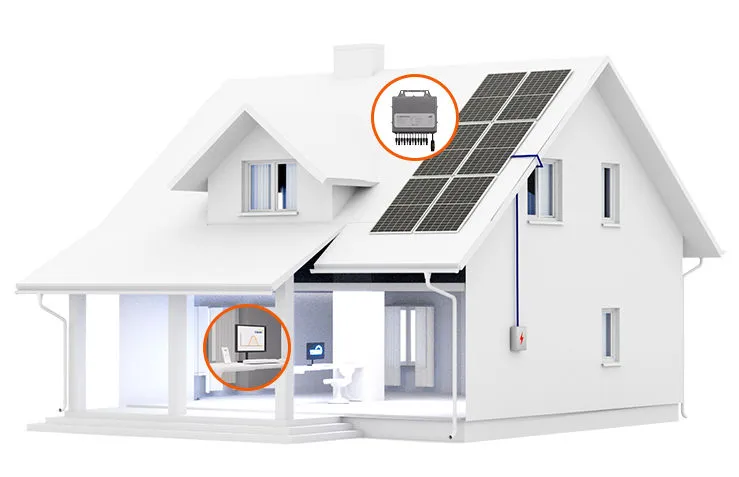

 LEARN MORE
LEARN MORE